For even more info, go to File- System Report. In the new window that appears, click Memory in the list on the left. It will show you the number of slots and what's in each one. In the below screenshot, there is one empty bank. It's the one with the Size, Type, Speed, and Status as Empty. Apr 07, 2018 Linux FAQ: How can I find Linux processor and memory information? (Also written as, How can I find Linux CPU information?, How can I find Linux RAM information?) Back to top How to show the Linux CPU/processor. To see what type of processor/CPU your computer system has, use this Linux command: cat /proc/cpuinfo. @azorius (and probably unimplemented) means the bios/chipset can handle 4 slots, but the board manufacturer decided not to include 2 of the possible slots the bios can support in the physical realm that is the actual MB.
Linux is one of the most popular open source operating system and comes with huge set of commands. The most important and single way of determining the total available space of the physical memory and swap memory is by using “free” command.
The Linux “free” command gives information about total used and available space of physical memory and swap memory with buffers used by kernel in Linux/Unix like operating systems.
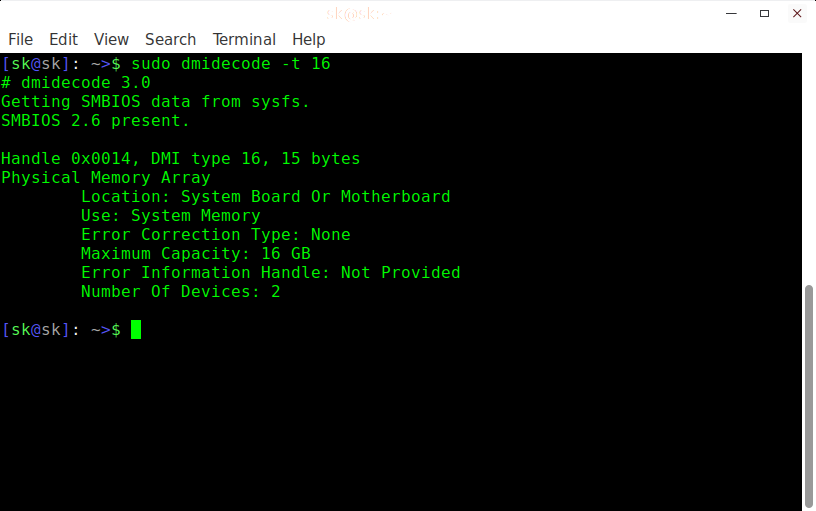
This article provides some useful examples of “free” commands with options, that might be useful for you to better utilize memory that you have.
1. Display System Memory
Free command used to check the used and available space of physical memory and swap memory in KB. See the command in action below.
2. Display Memory in Bytes
Free command with option -b, display the size of memory in Bytes.
3. Display Memory in Kilo Bytes
Free command with option -k, display the size of memory in (KB) Kilobytes.
4. Display Memory in Megabytes
To see the size of the memory in (MB) Megabytes use option as -m.
5. Display Memory in Gigabytes
Using -g option with free command, would display the size of the memory in GB(Gigabytes).
6. Display Total Line
Free command with -t option, will list the total line at the end.
7. Disable Display of Buffer Adjusted Line
By default the free command display “buffer adjusted” line, to disable this line use option as -o.
8. Display Memory Status for Regular Intervals
The -s option with number, used to update free command at regular intervals. For example, the below command will update free command every 5 seconds.
9. Show Low and High Memory Statistics
The -l switch displays detailed high and low memory size statistics.

10. Check Free Version
The -V option, display free command version information.
Read Also
Top Command, Find Command, Netstat Command.
Linux Find Out Memory Slots Without
The output should look something like this:
Here's an example output for the command above:
Memory Slots Available
Also see: How To Get Hardware Information In Linux